Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
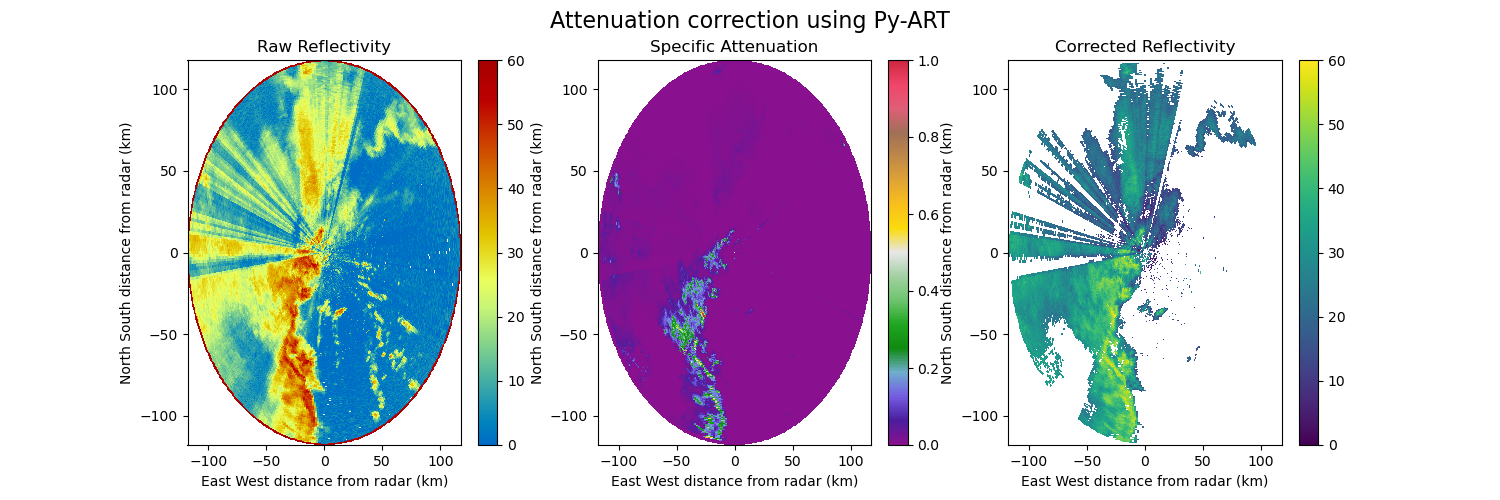
Correct reflectivity attenuation#
In this example the reflectivity attenuation is calculated and then corrected for a polarimetric radar using a Z-PHI method implemented in Py-ART.
print(__doc__)
# Author: Jonathan J. Helmus (jhelmus@anl.gov)
# License: BSD 3 clause
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import xradar as xd
import pyart
file = pyart.testing.get_test_data("sgpcsaprsurcmacI7.c0.20110520.095101.nc")
# read in the data
tree = xd.io.open_cfradial1_datatree(file)
radar = tree.pyart.to_radar()
# remove existing corrections
radar.fields.pop("specific_attenuation")
radar.fields.pop("corrected_reflectivity_horizontal")
# perform attenuation correction
spec_at, cor_z = pyart.correct.calculate_attenuation(
radar,
0,
refl_field="reflectivity_horizontal",
ncp_field="norm_coherent_power",
rhv_field="copol_coeff",
phidp_field="proc_dp_phase_shift",
)
radar.add_field("specific_attenuation", spec_at)
radar.add_field("corrected_reflectivity_horizontal", cor_z)
# create the plot
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15, 5))
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(131)
display = pyart.graph.RadarDisplay(radar)
display.plot(
"reflectivity_horizontal",
0,
ax=ax1,
vmin=0,
vmax=60.0,
colorbar_label="",
title="Raw Reflectivity",
)
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(132)
display.plot(
"specific_attenuation",
0,
vmin=0,
vmax=1.0,
colorbar_label="",
ax=ax2,
title="Specific Attenuation",
)
ax3 = fig.add_subplot(133)
display = pyart.graph.RadarDisplay(radar)
display.plot(
"corrected_reflectivity_horizontal",
0,
vmin=0,
vmax=60.0,
colorbar_label="",
ax=ax3,
title="Corrected Reflectivity",
)
plt.suptitle("Attenuation correction using Py-ART", fontsize=16)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (5 minutes 0.882 seconds)