Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Cloud Base Height Retrievals#
This example shows how to calculate the cloud base heights using the sobel edge detection method. This can be used for vertical radar and lidar data.
Author: Adam Theisen
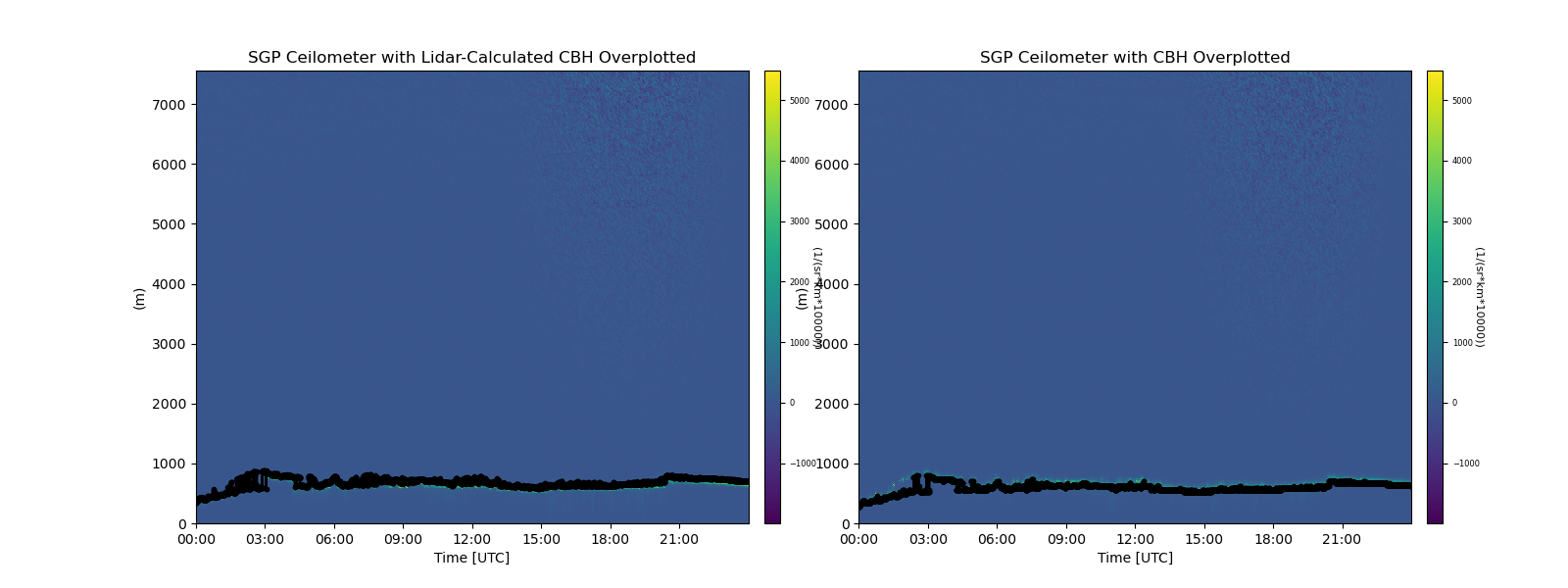
Average difference between ceilomter and sobel heights 84.37419
import numpy as np
from arm_test_data import DATASETS
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import act
# Read Ceilometer data for an example
filename_ceil = DATASETS.fetch('sgpceilC1.b1.20190101.000000.nc')
ds = act.io.arm.read_arm_netcdf(filename_ceil)
ds = act.retrievals.cbh.generic_sobel_cbh(
ds, variable='backscatter', height_dim='range', var_thresh=1000.0, fill_na=0.0
)
# Plot the cloud base height data
display = act.plotting.TimeSeriesDisplay(ds, subplot_shape=(1, 2), figsize=(16, 6))
display.plot('backscatter', subplot_index=(0, 0))
title = 'SGP Ceilometer with Lidar-Calculated CBH Overplotted'
display.plot('first_cbh', subplot_index=(0, 0), color='k', set_title=title)
display.plot('backscatter', subplot_index=(0, 1))
title = 'SGP Ceilometer with CBH Overplotted'
display.plot('cbh_sobel_backscatter', color='k', subplot_index=(0, 1), set_title=title)
diff = ds['first_cbh'].values - ds['cbh_sobel_backscatter'].values
print("Average difference between ceilomter and sobel heights ", np.nanmean(diff))
ds.close()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 4.975 seconds)