Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Working with TAR and gunzip files#
This is an example of how to use the TAR and gunzip extensions for creating or extracting data files. The functions for creation and extraction can be called independently to manage the data files directly or a TAR or gunzip file can be provided to the netCDF reader and the extraction will happen automatically to a temporary area.
Created TAR file: temporary_directory/created_tarfile.tar
New gunzip file: temporary_directory/created_tarfile.tar.gz
Extracted filenames: ['/home/runner/work/ACT/ACT/examples/utils/temporary_directory/tmpr91qtf11/sgpmetE13.b1.20190101.000000.cdf', '/home/runner/work/ACT/ACT/examples/utils/temporary_directory/tmpr91qtf11/sgpmetE13.b1.20190102.000000.cdf', '/home/runner/work/ACT/ACT/examples/utils/temporary_directory/tmpr91qtf11/sgpmetE13.b1.20190103.000000.cdf', '/home/runner/work/ACT/ACT/examples/utils/temporary_directory/tmpr91qtf11/sgpmetE13.b1.20190104.000000.cdf', '/home/runner/work/ACT/ACT/examples/utils/temporary_directory/tmpr91qtf11/sgpmetE13.b1.20190105.000000.cdf', '/home/runner/work/ACT/ACT/examples/utils/temporary_directory/tmpr91qtf11/sgpmetE13.b1.20190106.000000.cdf', '/home/runner/work/ACT/ACT/examples/utils/temporary_directory/tmpr91qtf11/sgpmetE13.b1.20190107.000000.cdf']
LS of temporary directory: [PosixPath('temporary_directory/tmpr91qtf11')]
LS of temporary directory: []
from pathlib import Path
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Import standard libraries
from arm_test_data import DATASETS
# Import ACT functions
from act.io.arm import read_arm_netcdf
from act.plotting import TimeSeriesDisplay
from act.utils.io_utils import cleanup_files, pack_gzip, pack_tar, unpack_tar
# Create a TAR file from multiple netCDF data files and pass newly created
# TAR file into read_arm_netcdf() to be unpacked and read.
# Here we get a list of MET data files to pack into a TAR bundle
met_wildcard_list = [
'sgpmetE13.b1.20190101.000000.cdf',
'sgpmetE13.b1.20190102.000000.cdf',
'sgpmetE13.b1.20190103.000000.cdf',
'sgpmetE13.b1.20190104.000000.cdf',
'sgpmetE13.b1.20190105.000000.cdf',
'sgpmetE13.b1.20190106.000000.cdf',
'sgpmetE13.b1.20190107.000000.cdf',
]
met_files = [Path(DATASETS.fetch(file)) for file in met_wildcard_list]
# We can pass the list of netCDF data files to the pack_tar() function.
# Notice that the new_dir directory does not exist. The directory will
# be created.
new_dir = 'temporary_directory'
filename = pack_tar(met_files, write_directory=new_dir)
print('Created TAR file: ', filename)
# Read the data within the TAR file
ds = read_arm_netcdf(filename)
# Create a plotting display object
display = TimeSeriesDisplay(ds, figsize=(15, 10), subplot_shape=(1,))
# Plot up the diffuse variable in the first plot
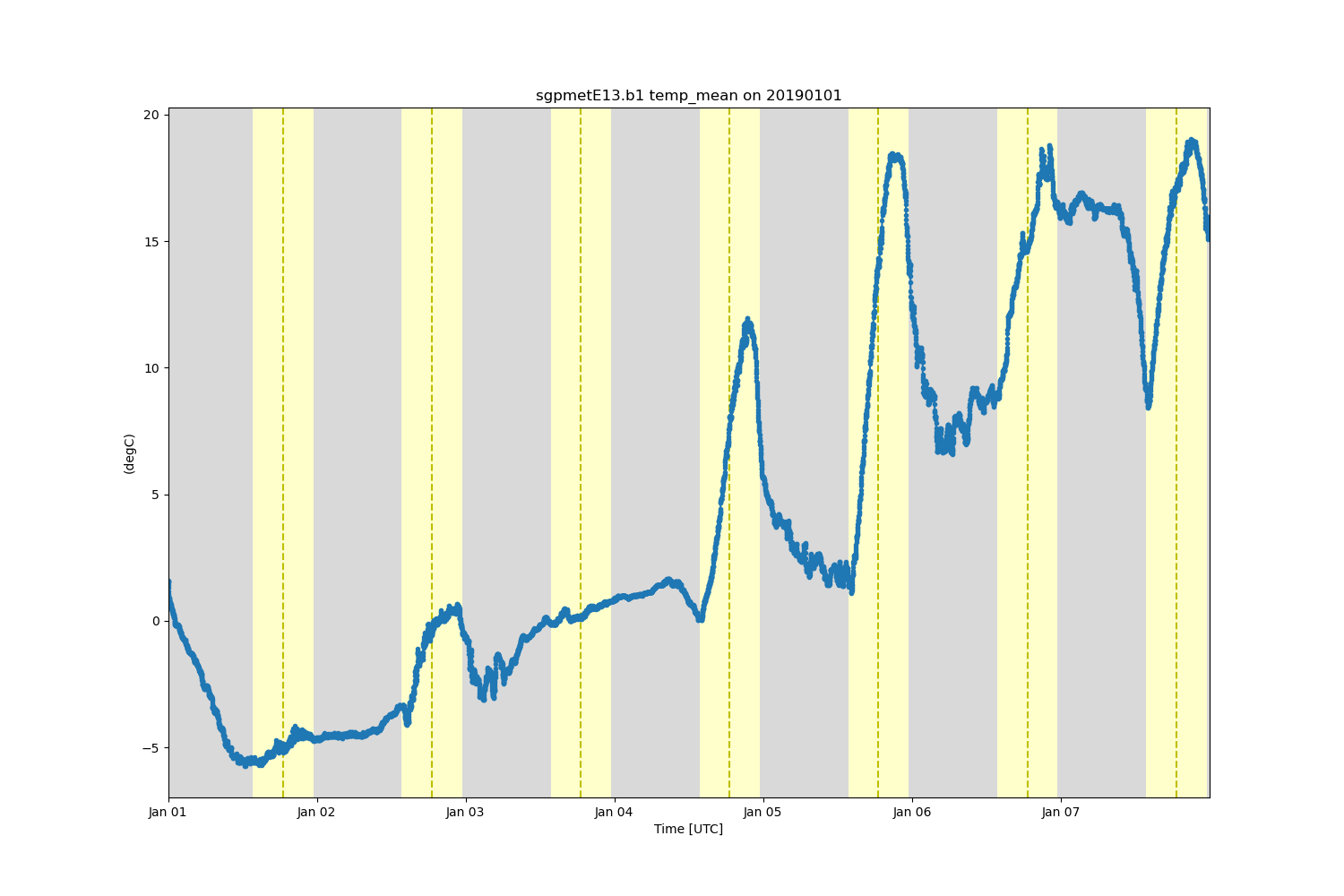
variable = 'temp_mean'
display.plot(variable, subplot_index=(0,), day_night_background=True)
plt.show()
del ds
# Create a gunzip file from TAR file containing multiple netCDF data files and
# pass newly created gunzip file into read_arm_netcdf() to be unpacked and read.
# Pass the TAR filename into gunzip. Have the function remove the TAR file after
# creating the gunzip file
filename = pack_gzip(filename, write_directory=new_dir, remove=True)
print('New gunzip file: ', filename)
# Read the data within the gunzipped TAR file
ds = read_arm_netcdf(filename)
# Create a plotting display object
display = TimeSeriesDisplay(ds, figsize=(15, 10), subplot_shape=(1,))
# Plot up the diffuse variable in the first plot
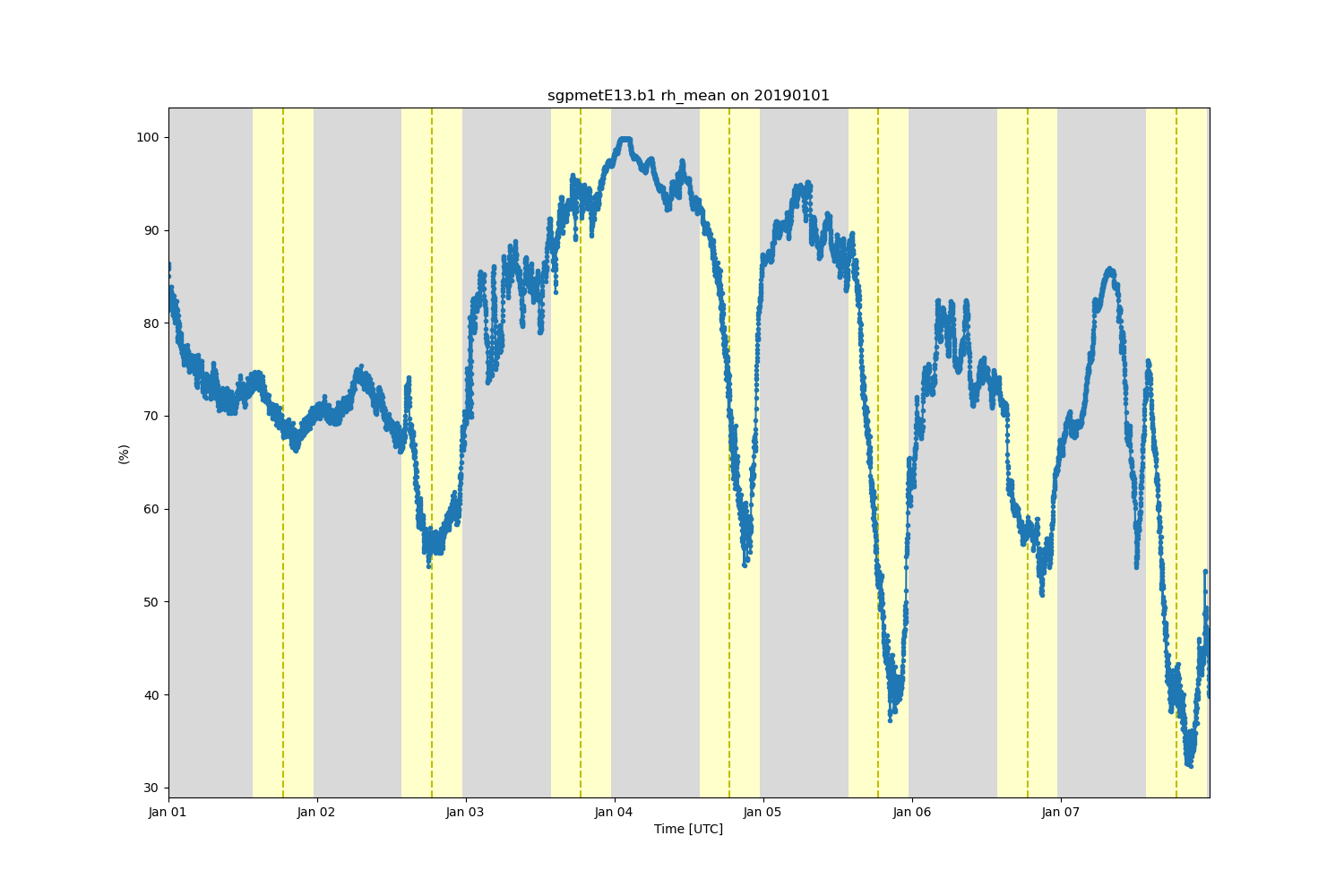
variable = 'rh_mean'
display.plot(variable, subplot_index=(0,), day_night_background=True)
plt.show()
Path(filename).unlink()
# When working with a TAR file and reading it often will be more efficient to untar once
# and point reader to untarred files. Then clean up the directory when multiple reads are done.
tar_file = pack_tar(met_files, write_directory=new_dir)
# This will unpack the TAR file to a new directroy created with a random name to ensure multiple
# simultaneous uses do not collide. The full path to all extracted filenames will be returned.
filenames = unpack_tar(
tar_file, write_directory=new_dir, randomize=True, return_files=True, remove=True
)
# Print the extracted filenames
print('Extracted filenames: ', filenames)
# Print a list of filenames and directories in the new directory
print('LS of temporary directory:', list(Path(new_dir).glob('*')))
# After the extracted files are read for last time we can clean up the directory.
cleanup_files(files=filenames)
# Print a list of filenames and directories in the new directory
print('LS of temporary directory:', list(Path(new_dir).glob('*')))
# Remove the temporary directory we created to clean up directory.
Path(new_dir).rmdir()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.426 seconds)