Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Planetary Boundary Layer Height Gradient Method Retrievals#
This example shows how to estimate the planetary boundary layer height via a gradient method retrieval
Author: Joe O’Brien
from arm_test_data import DATASETS
import act
# Read Ceilometer data for an example
filename_ceil = DATASETS.fetch('sgpceilC1.b1.20190101.000000.nc')
ds = act.io.arm.read_arm_netcdf(filename_ceil)
# Apply corrections to the dataset
ds = act.corrections.correct_ceil(ds, var_name='backscatter')
# Estimate PBL Height via a gradient method
ds = act.retrievals.pbl_lidar.calculate_gradient_pbl(ds, parm="backscatter", smooth_dis=3)
# Estimate PBL Height via a modified gradient method
ds = act.retrievals.pbl_lidar.calculate_modified_gradient_pbl(
ds, parm="backscatter", threshold=1e-4, smooth_dis=3
)
# Plot the pbl height estimates
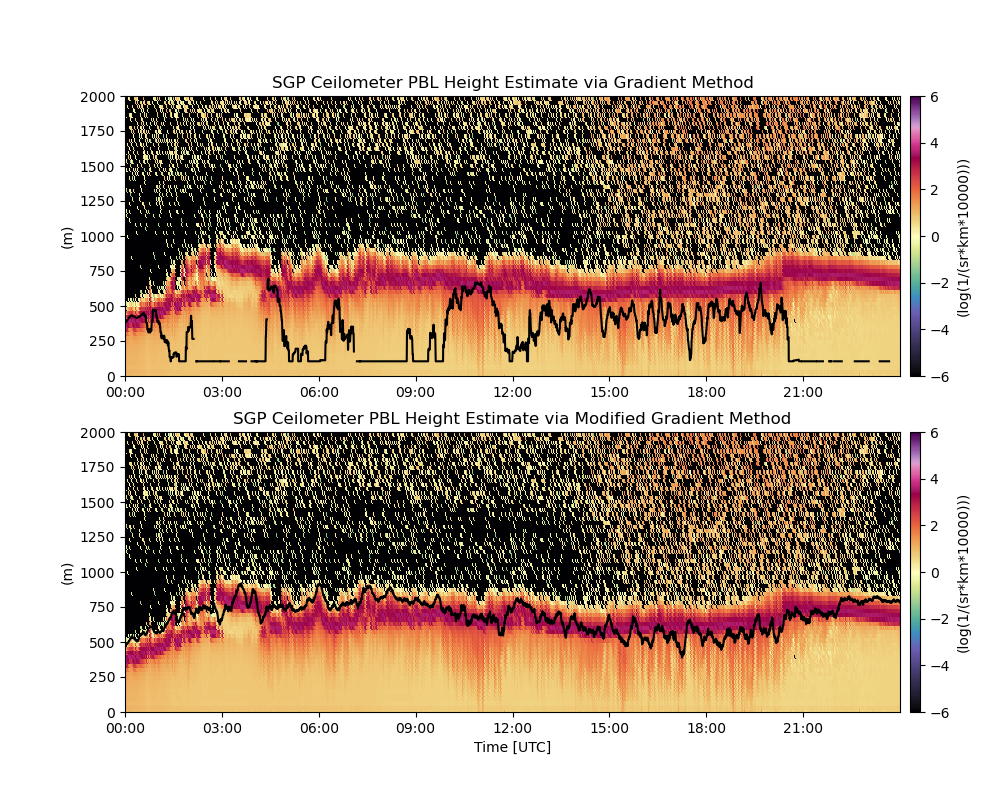
display = act.plotting.TimeSeriesDisplay(ds, subplot_shape=(2,), figsize=(10, 8))
# plot the CL backscatter before overlaying the Gradient Method PBL Height
display.plot(
'backscatter',
subplot_index=(0,),
cmap='ChaseSpectral',
vmin=-6,
vmax=6,
set_title='SGP Ceilometer PBL Height Estimate via Gradient Method',
)
# overlay the PBL Height estimate, compute ~10min temporal averages
display.axes[0].plot(
ds['time'].values,
ds['pbl_gradient'].rolling(time=38, min_periods=3, center=True).mean().values,
color='k',
)
# shorten the range
display.set_yrng([0, 2000], subplot_index=(0,))
# plot the CL backscatter before overlaying the Modified Gradient PBL Height
display.plot(
'backscatter',
subplot_index=(1,),
cmap='ChaseSpectral',
vmin=-6,
vmax=6,
set_title='SGP Ceilometer PBL Height Estimate via Modified Gradient Method',
)
# overlay the PBL Height estimate, compute ~10min temporal averages
display.axes[1].plot(
ds['time'].values,
ds['pbl_mod_gradient'].rolling(time=38, min_periods=3, center=True).mean().values,
color='k',
)
# shorten the range
display.set_yrng([0, 2000], subplot_index=(1,))
Total running time of the script: (10 minutes 32.253 seconds)